Before you get started!
Welcome to OpenStack!
In this series of tutorials, we will walk you through all the necessary steps to install, configure and get started with OpenStack. Using just a single machine, you will learn how to use OpenStack for cloud infrastructure implementation purposes, from a single-node installation to large-scale clusters.
This tutorial is the fifth in the “Phase 1 - Learn OpenStack” series.
What is OpenStack?
OpenStack is a collection of open source projects designed to work together to form the basis of a cloud. OpenStack can be used for both private and public cloud implementation.
What is Sunbeam?
Sunbeam is an upstream project under the governance of the OpenInfra Foundation (OIF), which was created to lower the barrier to entry for OpenStack, simplify its adoption process, and set the foundation for an autonomous private cloud. Sunbeam uses cloud-native architecture and total bottom-up automation to make OpenStack more accessible to newcomers and to help users get to grips with the platform immediately.
What is MicroStack?
MicroStack (based on Sunbeam) is an OpenStack distribution designed for small-scale cloud environments. While it is available with full commercial support from Canonical, it can also be self-deployed with no friction, effectively eliminating the need for a paid consulting engagement. MicroStack currently includes core OpenStack services only, but is expected to evolve quickly to ensure full feature parity with Canonical’s Charmed OpenStack soon.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to:
- Distinguish between the various instance templates
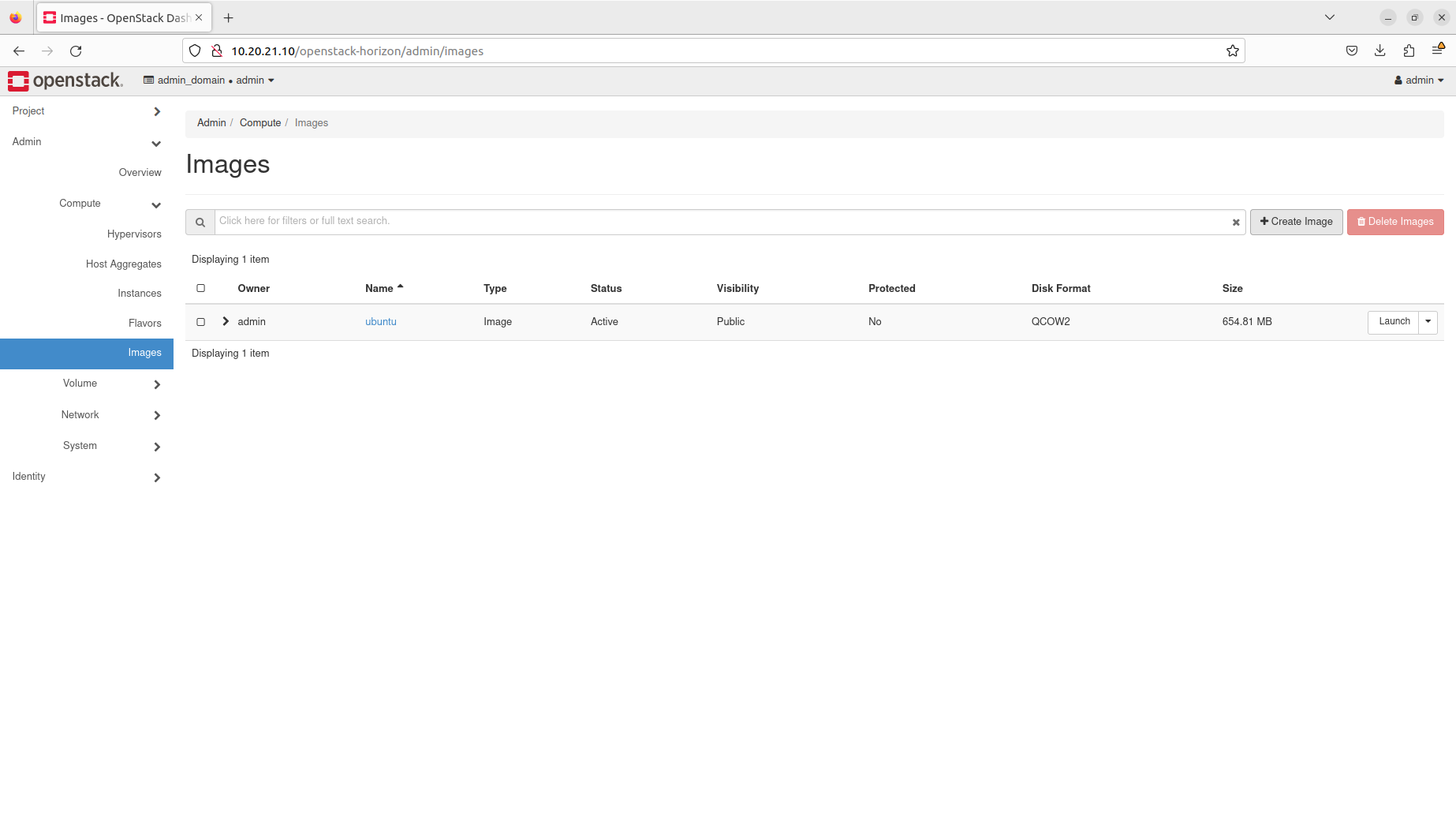
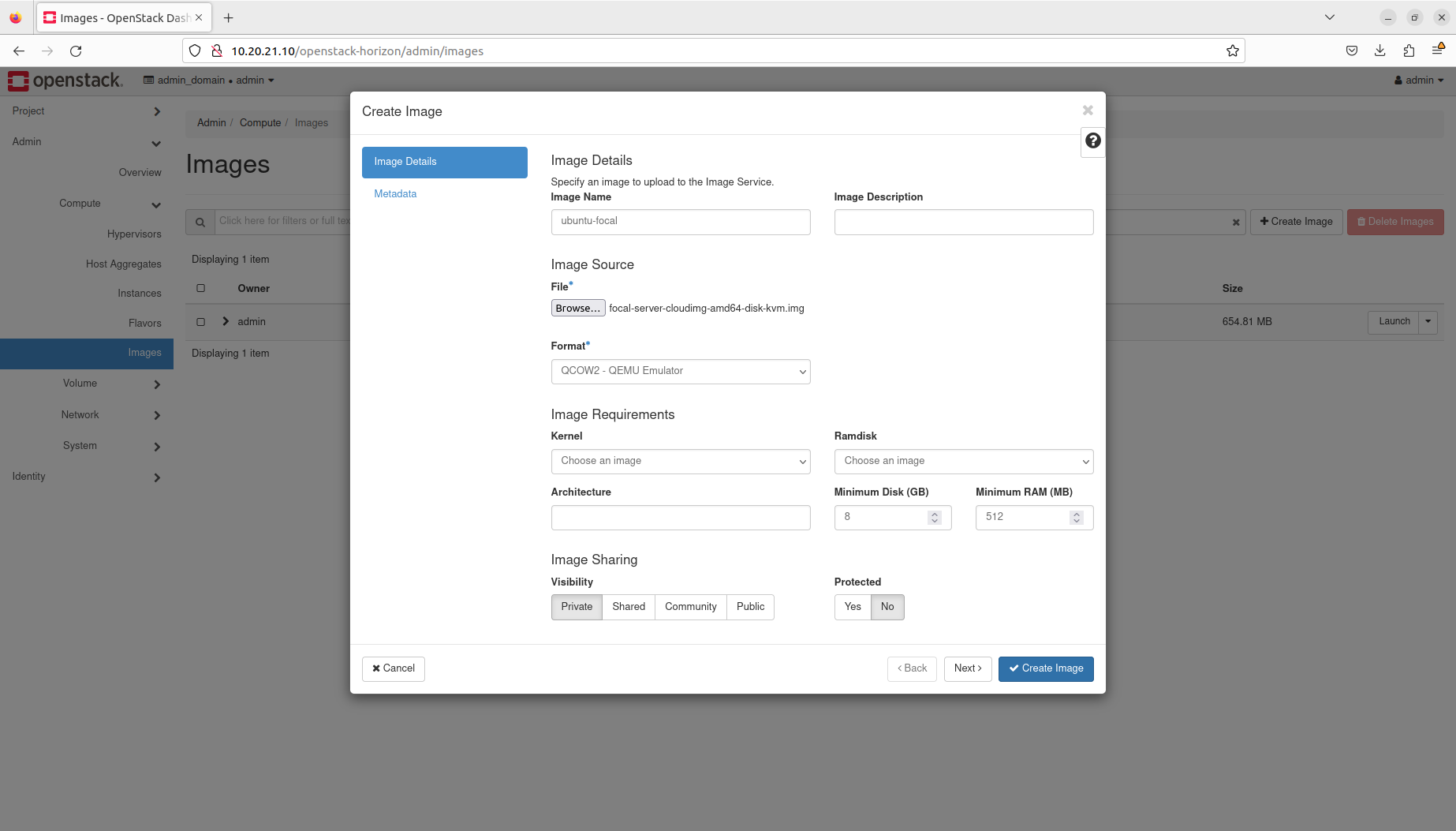
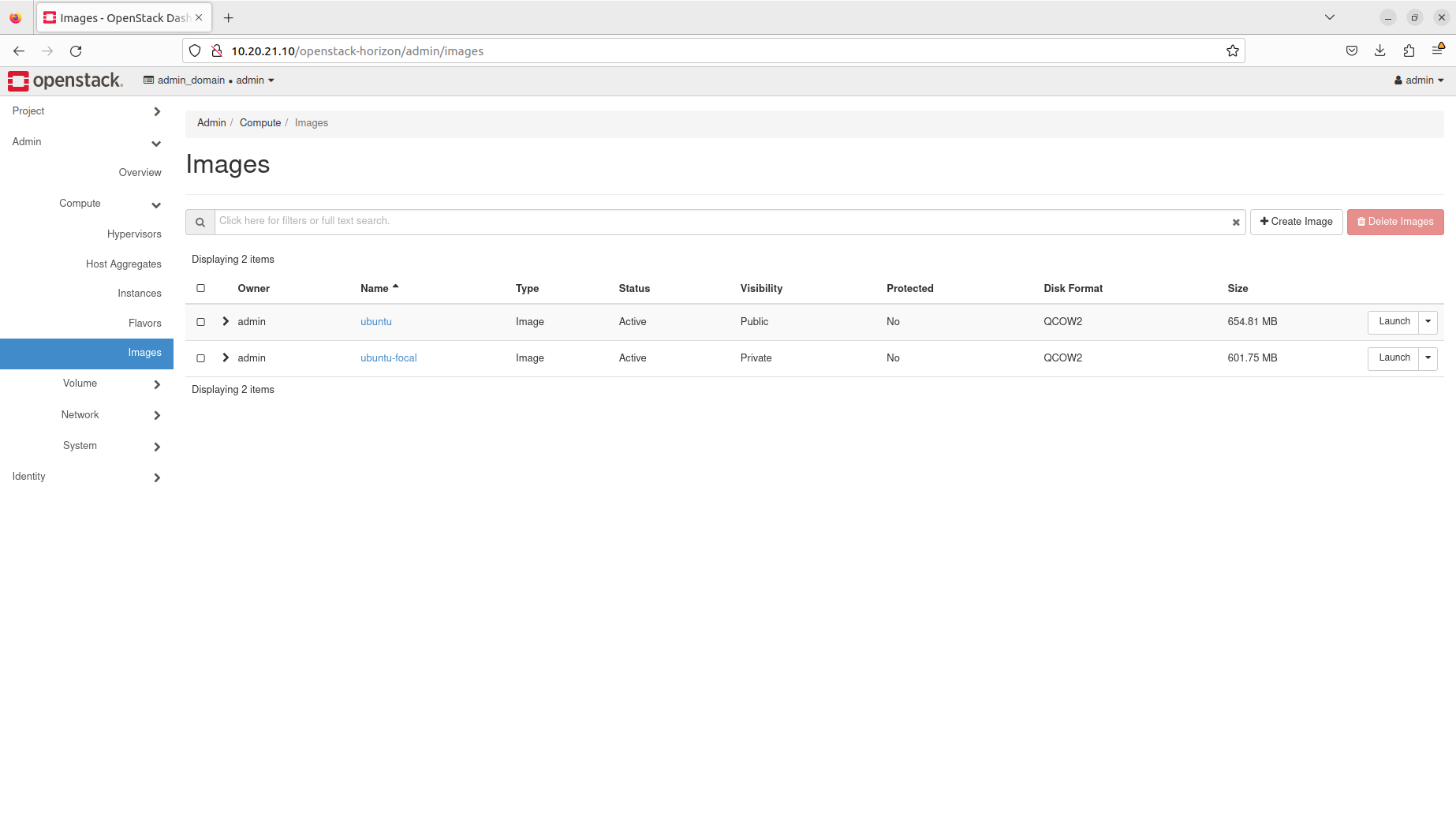
- Manage images
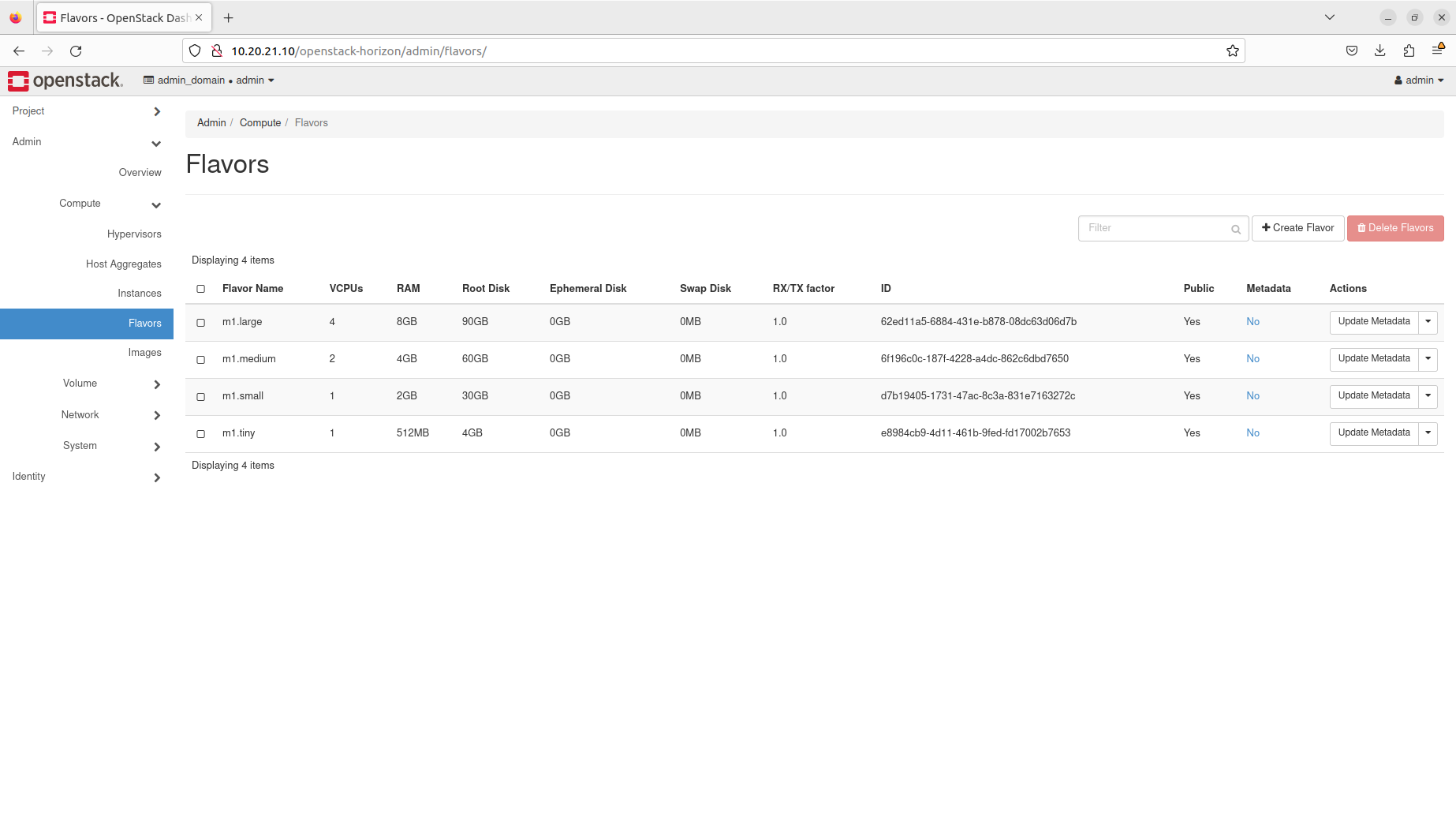
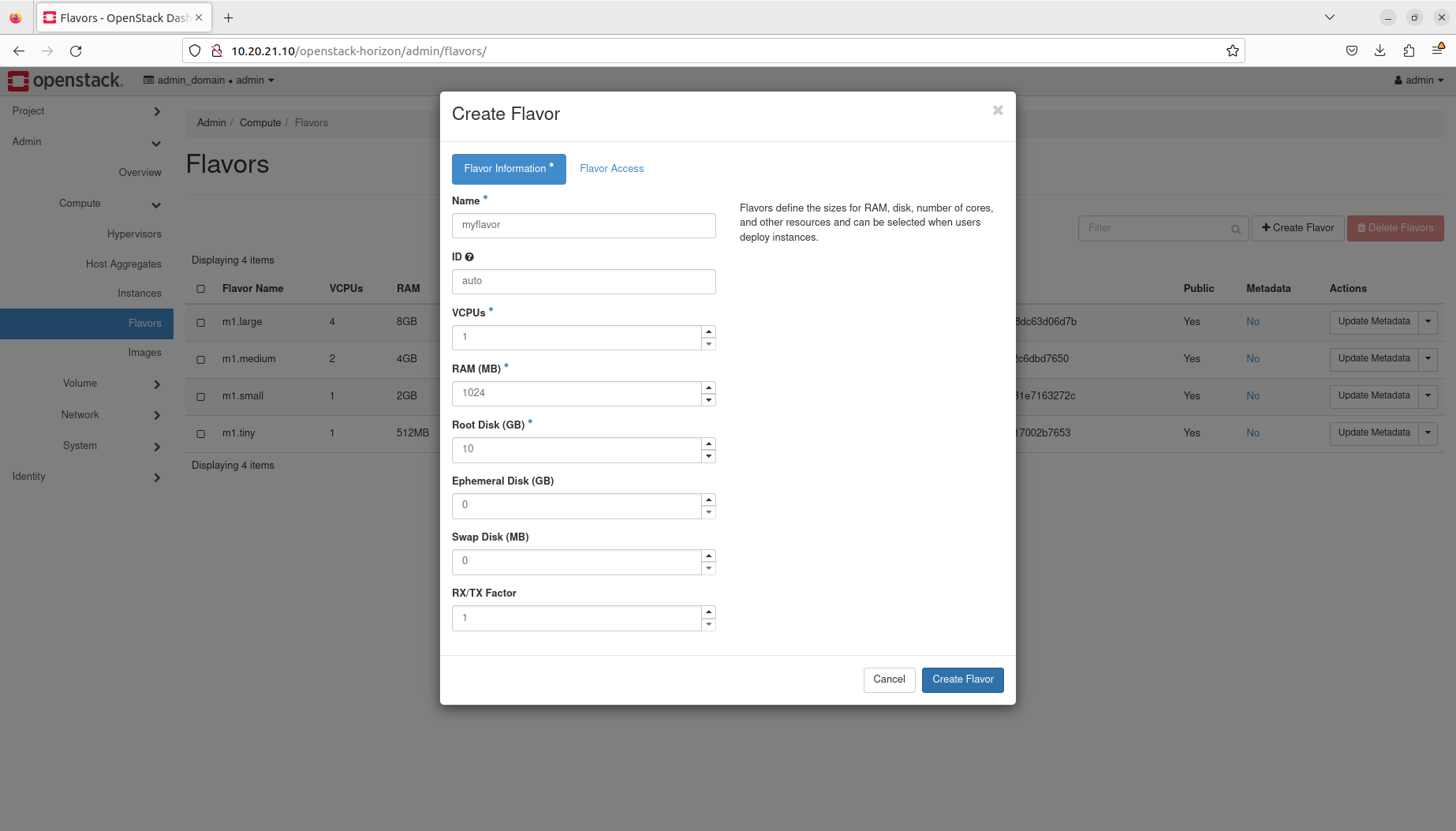
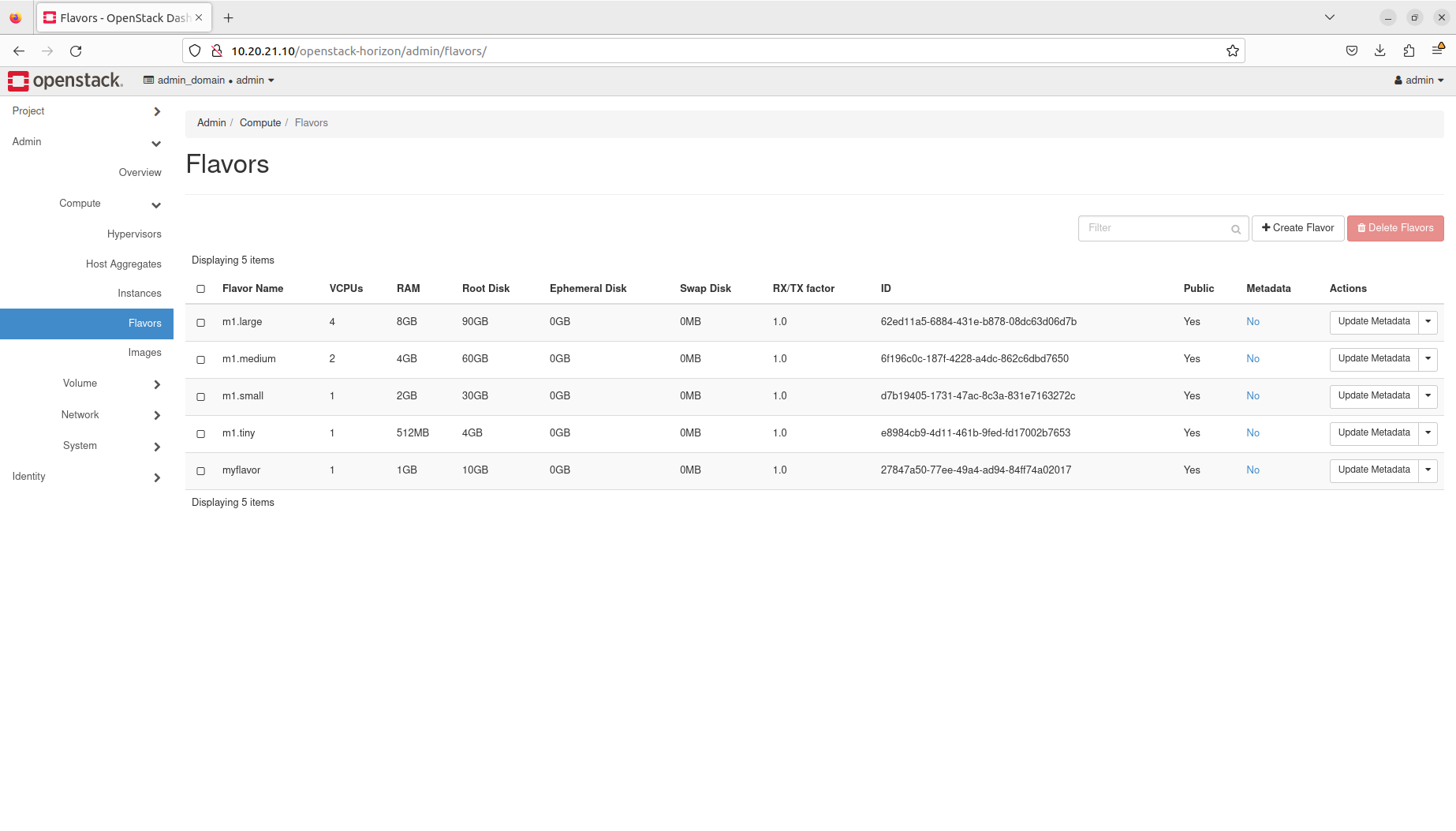
- Manage flavors
You will only need:
One fresh physical or virtual machine with:
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS installed,
- Static IP address assigned to its primary network interface,
- OpenSSH server installed and configured,
- 4+ core amd64 CPU,
- 16 GB of RAM,
- 50 GB of SSD storage.
- OpenStack cloud bootstrapped, configured and sample instance launched,
- OpenStack client set up.